Understanding Classic Tweed Coats
Tweed fabric represents one of the most enduring textile traditions in menswear, with deep roots in the highlands of Scotland and rural Ireland. This distinctive woolen cloth emerged as a practical solution to the harsh weather conditions faced by farmers, hunters, and outdoor workers in the British Isles. Traditional tweed production involves carding raw wool, spinning it into yarn, and then weaving it into complex patterns that give tweed its characteristic appearance.
Classic tweed is composed of 100% wool, typically from hardy sheep breeds whose fibers possess natural resilience. What truly sets tweed apart is its unique weaving patterns – herringbone with its distinctive V-shaped rows, houndstooth featuring its broken checkered pattern, and barleycorn with its textured, three-dimensional appearance. These patterns weren’t merely decorative; they added structural integrity and enhanced the fabric’s weatherproofing qualities.
The traditional silhouette of a tweed coat reflects its practical origins – substantial, structured, and designed to withstand harsh elements. Early tweed coats featured roomy cuts allowing for layers underneath, sturdy collars that could be turned up against the wind, and often leather reinforcements at stress points.
What makes men’s tweed coats immediately recognizable is their distinctive tactile quality. The fabric has a substantial hand-feel with a slightly rough texture that comes from the coarse wool fibers. This textural element isn’t a defect but rather a hallmark of authentic tweed, providing both character and functionality.
Perhaps the most famous tweed variant is Harris Tweed, which enjoys protected status and must be handwoven by islanders in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland using traditional methods. Donegal tweed from Ireland is known for its characteristic flecks of color throughout the weave, while traditional colors tend toward earthy tones – heathery purples, mossy greens, and warm browns – often reflecting the natural landscape that inspired them.
Understanding the rich heritage and distinctive characteristics of classic tweed patterns provides essential context before we compare these traditional garments with their modern wool counterparts.
Key Characteristics of Traditional Tweed Coats
When evaluating a traditional tweed coat, several performance characteristics stand out that explain its centuries of popularity despite technological advancements in textile production.
Exceptional Durability: Tweed’s reputation for longevity is well-earned. The tightly woven structure creates a fabric that resists tears, abrasion, and general wear. A quality tweed coat often becomes a multi-generational heirloom, developing character with age rather than simply wearing out. The natural crimp and elasticity of wool fibers allow them to return to shape after stretching, preventing the saggy appearance that plagues many other fabrics.
Natural Weather Resistance: Even without modern treatments, traditional tweed offers impressive protection against the elements:
* Water-repellent properties come from lanolin, the natural oil in wool, and the tight weave that prevents water penetration
* Wind resistance results from the dense fabric structure that blocks air movement
* Thermal insulation through air pockets trapped within the textured weave
Superior Thermal Performance: Tweed coats excel in cold conditions due to wool’s exceptional insulating properties. The fabric traps body heat effectively while still allowing some breathability to prevent overheating. This natural temperature regulation works in multiple conditions, making tweed surprisingly versatile across seasons.
Substantial Weight and Structure: Traditional tweed coats are noticeably heavier than modern alternatives, typically weighing between 700-900 grams per meter of fabric. This weight contributes to both durability and warmth, while also providing a distinctive drape and silhouette that’s immediately recognizable.
Surprising Breathability: Despite its substantial construction, tweed allows moisture vapor to escape, preventing the clammy feeling associated with many synthetic waterproof materials. This breathability comes from wool’s natural ability to absorb moisture from the skin and release it to the outside environment.
The performance characteristics of tweed were proven through centuries of use in country sports like hunting and fishing, where wearers faced unpredictable weather conditions and needed clothing that could withstand rugged use. These inherent qualities provide the baseline against which modern wool coat innovations must be measured.
Popular Tweed Coat Styles for Men
Tweed’s versatility has allowed it to evolve into various coat styles, each with distinctive features suited to different contexts:
Traditional Tweed Overcoats
* Full-length design extending below the knee for maximum coverage
* Often feature notched lapels and a single or double-breasted front
* Structured shoulders and a slightly tailored waist
* Classic color patterns like herringbone or houndstooth
Hunting/Field Jackets
* Shorter length for ease of movement
* Action back design with pleating for arm mobility
* Functional details like leather shooting patches on shoulders
* Multiple pockets for carrying hunting accessories
* Often in more muted earth tones to blend with natural surroundings
Tweed Blazers and Sport Coats
* Medium weight for indoor-outdoor versatility
* Often feature elbow patches for durability
* Single-breasted design with notched lapels
* Suitable for business casual and smart casual settings
Contemporary Tweed Interpretations
* Slimmer cuts with less structure than traditional versions
* Lighter weight tweed fabrics for greater comfort
* Modern details like zip closures or minimalist designs
* Often blended with other fibers for enhanced performance
Each style serves a specific purpose, from formal business wear to rugged outdoor activities. The enduring appeal of men’s wool coats in tweed variations speaks to both the material’s functionality and its timeless aesthetic appeal, which continues to influence modern outerwear design.
Exploring Modern Wool Coat Construction
Modern wool coats represent a significant departure from traditional tweed while maintaining wool as their primary material. What distinguishes a “modern wool coat” is not merely its contemporary design but fundamental differences in material processing, fabric construction, and performance enhancements.
Premium Wool Varieties
Today’s finest wool coats utilize specialized wool types selected for specific performance characteristics:
- Merino Wool: Featuring fibers significantly finer than traditional wool (often under 24 microns), merino provides exceptional softness while maintaining insulation properties
- Cashmere Blends: Incorporating goat-derived cashmere fibers for luxurious softness and enhanced thermal properties
- Lambswool: Harvested from young sheep for a softer hand-feel while retaining durability
Manufacturing Innovations
Modern production techniques have revolutionized how wool performs:
- Super-fine milling processes that create smoother, lighter fabrics without sacrificing warmth
- Computerized weaving technology allowing precise, consistent fabric construction
- Heat-setting techniques that enhance fabric stability and shape retention

Performance Enhancements
Contemporary wool coats often incorporate treatments that address traditional wool’s limitations:
- DWR (Durable Water Repellent) finishes that enhance water resistance without compromising breathability
- Anti-pilling treatments that maintain a smooth surface appearance
- Pre-shrinking processes that improve dimensional stability
- Stain-resistant coatings that protect against everyday contaminants
Strategic Blending
Unlike pure tweed, modern wool coats frequently incorporate other fibers to enhance performance:
- Wool/polyester blends for wrinkle resistance and quicker drying
- Wool/nylon combinations for increased durability and reduced weight
- Wool/cashmere blends balancing luxury with practicality
Understanding the differences between merino wool and regular wool coats helps explain why modern wool garments can be significantly lighter—often 30-50% less weight than traditional tweed—while still providing effective insulation. These technological advancements represent not just aesthetic updates but fundamental reimagining of what wool outerwear can achieve in terms of comfort, performance, and versatility.
Contemporary Wool Coat Styles and Designs
Modern wool coat designs embrace minimalism, technical performance, and versatile styling options that contrast sharply with traditional tweed aesthetics:
Minimalist Tailored Overcoats
* Clean, uncluttered front with hidden or minimal closures
* Absence of decorative elements like contrast stitching or visible patterns
* Precise tailoring with structured shoulders and tapered waist
* Often in solid neutral colors (charcoal, navy, camel)
Technical Wool Blend Performance Coats
* Athletic-inspired cuts allowing greater range of motion
* Strategic articulation at elbows and shoulders
* Hidden technical features like waterproof membranes
* Often incorporate reflective elements or adjustable features
Casual Wool Classics Reimagined
* Modern pea coats with slimmer proportions than traditional versions
* Car coats with cleaner lines and minimalist details
* Bomber and varsity-inspired wool jackets for casual sophistication
* Duffle coats with updated proportions and refined toggles
Luxury Premium Wool Designs
* Ultra-fine wool and cashmere blend fabrics with exceptional drape
* Meticulous hand-finishing details
* Minimalist exteriors with sumptuous linings
* Often feature unusual closures or architectural elements
Contemporary Silhouettes
* Slim-fit designs that create a streamlined appearance
* Drop-shoulder construction for a relaxed, modern aesthetic
* Cropped lengths that work well with contemporary trouser styles
* Oversized options that layer effectively over multiple garments
Men’s wool blend coats demonstrate how modern design approaches have evolved wool outerwear beyond traditional boundaries. These contemporary styles prioritize versatility, ease of wear, and refined aesthetics that integrate seamlessly with today’s wardrobes, creating clear visual distinction from their tweed predecessors.
Head-to-Head Comparison: Weather Performance and Durability
When evaluating tweed against modern wool coats for practical performance, several key factors determine which material might better serve your needs:
| Performance Factor | Traditional Tweed | Modern Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Rain Resistance | Moderate natural water resistance; becomes heavy when saturated | Variable; often features DWR treatment but may need reapplication |
| Wind Protection | Excellent due to dense weave | Good to excellent depending on weave tightness |
| Cold Weather Insulation | Superior for dry cold; heavy but effective | Very good; often lighter with comparable warmth |
| Durability at Stress Points | Excellent; naturally reinforced by weave structure | Variable; depends on construction quality |
| Weight When Wet | Heavy; slow to dry | Moderate; typically dries faster than tweed |
| Long-term Shape Retention | Excellent; maintains structure for decades | Variable; depends on wool quality and construction |
Tweed demonstrates exceptional performance in harsh, dry cold conditions where its weight becomes an advantage rather than a liability. The natural oils in wool fibers and tight weave structure create inherent weather resistance without additional treatments. However, in prolonged rain, tweed becomes heavy and can take considerable time to dry completely.
Modern wool coats often incorporate technological enhancements to address traditional limitations. Water-resistant treatments help moisture bead up and roll off rather than saturating the fabric. However, these treatments require periodic reapplication to maintain effectiveness, creating ongoing maintenance requirements that traditional tweed doesn’t have.
For durability, traditional tweed often excels through its robust construction and inherently strong weave patterns. These coats frequently last for decades with minimal signs of wear at common failure points like elbows and cuffs. Modern wool coats vary significantly in durability based on construction quality and material composition – pure wool versions tend to outperform blends in longevity, though they may require more careful maintenance.
Climate considerations should heavily influence your choice. Wool coats for cold climates demand different performance attributes than those for mild or wet conditions. Tweed generally excels in cold, windy environments where its weight and structure provide superior insulation. Modern wool offers better versatility across variable conditions, particularly in transitional seasons or regions with fluctuating weather patterns.
Style Versatility: When Each Coat Type Shines
The distinct aesthetic qualities of tweed and modern wool coats make each suitable for different style contexts and personal expression.
Formal Business Settings
Tweed projects traditional authority but can appear overly rustic in contemporary corporate environments. Modern wool overcoats in solid dark colors offer cleaner lines that complement today’s tailored suits better. The exception is heritage professional environments (law, finance, academia) where tweed’s traditional associations remain advantageous.
Urban Casual Contexts
Modern wool coats typically integrate more seamlessly with contemporary city wardrobes. Their cleaner lines and lighter weight work well when navigating public transportation or moving between indoor and outdoor environments frequently. Slim-cut modern wool coats particularly complement the narrower silhouettes of current casual wear.

Rural and Outdoor Environments
Tweed remains unmatched for authentic country style. Its rugged texture harmonizes with casual outdoor clothing, and its durability withstands rough treatment. The distinctive patterns also tend to show less dirt and wear than solid-colored modern wool coats when used in genuine outdoor activities.
Seasonal Transitions
Modern wool coats generally offer more versatility for layering. Their lighter weight allows them to work in both deep winter (over multiple layers) and transitional seasons (over lighter clothing). Tweed coats, being inherently warmer and heavier, excel specifically in cold weather but can become cumbersome during seasonal transitions.
Men’s wool overcoats demonstrate particular versatility when styled thoughtfully. A charcoal wool overcoat pairs equally well with formal business attire or weekend denim, while tweed often reads as deliberately casual or traditional regardless of accompanying garments.
For developing a versatile wardrobe, modern wool coats typically offer greater adaptability across diverse settings. However, tweed provides distinctive character that makes a stronger style statement, particularly valuable for those seeking to project classical sophistication or heritage-inspired authenticity in their personal style.
Comfort Factors: Weight, Feel, and Wearability
The physical experience of wearing these different coat types significantly impacts satisfaction with your purchase and likelihood of regular use.
Weight Differences
Traditional tweed coats typically weigh between 3-5 pounds (1.4-2.3 kg), creating substantial presence on the body. This weight provides reassuring heft and excellent drape but can become tiring during extended wear. Modern wool coats generally weigh 1.5-3 pounds (0.7-1.4 kg), making them noticeably lighter and less physically demanding during all-day wear.
Tactile Comfort
Tweed’s characteristic texture feels substantial and slightly rough against other clothing layers, occasionally causing friction with more delicate fabrics underneath. The surface texture can also catch slightly on other fabrics. Modern wool, particularly merino-based versions, offers smoother interaction with underlying clothing and greater comfort when brushing against skin at neck and wrist openings.
Movement Restriction
Traditional tweed’s structured construction can limit range of motion, particularly in shoulders and arms. The substantial fabric creates a stiffer drape that requires breaking in over time. Modern wool coats, especially those with strategically placed stretch panels or relaxed shoulder construction, typically allow greater freedom of movement immediately from purchase.
Break-in Period
Tweed coats often require a considerable wearing period before conforming comfortably to the wearer’s body, sometimes taking an entire season to fully adapt. Quality tweed improves with wear, gradually molding to your movements and posture. Modern wool coats generally require minimal breaking in, offering their intended comfort level almost immediately.
All-Day Wearability
For extended wearing periods, modern wool typically offers superior comfort through lighter weight and greater flexibility. However, tweed provides unmatched insulation for stationary outdoor activities in cold conditions, where its weight becomes an advantage rather than a liability.
These comfort factors should be weighted according to your typical usage patterns. Those with active lifestyles involving frequent movement or travel may prioritize the lighter, more flexible qualities of modern wool. Those spending extended periods outdoors in cold conditions might find tweed’s substantial construction worth the additional weight.
Investment Value: Price, Longevity, and Cost-Per-Wear
Evaluating the financial proposition of tweed versus modern wool coats requires looking beyond initial price tags to consider total ownership value over time.
Initial Price Range
* Quality traditional tweed overcoats typically range from $350-$1,200
* Modern wool overcoats of comparable quality generally range from $250-$900
* Premium designer versions of either can exceed $2,000
Expected Lifespan
* Well-maintained traditional tweed coats regularly last 15-25+ years
* Quality modern wool coats typically last 7-15 years with proper care
* Wool blend versions with synthetic fibers generally show wear more quickly
Maintenance Economics
* Traditional tweed usually requires professional cleaning only 1-2 times per year ($20-50 annually)
* Modern wool coats often need more frequent cleaning, particularly lighter colors
* Tweed rarely requires repairs beyond occasional button replacement
* Modern wool may need seam repairs or reapplication of water-resistant treatments
Value Retention
* Heritage tweed brands maintain strong resale value, often recouping 40-60% of purchase price
* Modern wool coats typically depreciate more quickly in resale markets
* Vintage tweed coats from quality makers can sometimes appreciate in value
Calculating True Cost
To determine actual value, consider:
* Purchase price ÷ estimated wears before replacement
* Add annual maintenance costs
* Subtract potential resale value
* Consider versatility factor (more versatile pieces have lower cost-per-wear)
While modern wool coats generally offer lower initial investment, traditional tweed often provides superior long-term value through extended lifespan and lower maintenance requirements. For those planning ownership of 10+ years, tweed frequently represents better financial value despite higher upfront cost. However, if your style preferences change frequently or you prefer updating your wardrobe regularly, modern wool’s lower entry price may prove more economical.
Care and Maintenance Requirements Compared
Proper maintenance significantly impacts both the appearance and longevity of wool outerwear. Understanding the different care requirements helps set realistic expectations for ownership.
Tweed Care Requirements:
* Professional dry cleaning recommended only 1-2 times annually (excess cleaning removes natural oils)
* Spot cleaning with damp cloth effective for minor stains
* Air out after wear rather than cleaning (wool’s antimicrobial properties minimize odors)
* Brush with soft clothes brush to remove surface dirt and restore nap
* Store on sturdy wooden hangers to maintain shoulder structure
Modern Wool Care Requirements:
* Dry cleaning frequency varies by color and wear patterns (2-4 times annually typical)
* Some modern wool blends may permit careful hand washing (check manufacturer guidance)
* More susceptible to water staining, requiring faster response to precipitation
* May need reapplication of water-resistant treatments after cleaning
* Typically requires protection from moths just like tweed
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Tweed Solution | Modern Wool Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Moths | Cedar blocks, regular movement/airing | Same preventative measures |
| Pilling | Rarely an issue; remove with fabric shaver if occurs | More common; requires regular removal with fabric shaver |
| Odors | Natural antimicrobial properties; air out thoroughly | May retain odors more; occasional freshening sprays helpful |
| Storage | Breathable garment bag, cedar hangers | Similar requirements; lighter fabrics need better support |
The right coat length also affects maintenance requirements – longer coats show more wear at hems and may collect more environmental debris than shorter styles. When considering maintenance effort, tweed generally requires less frequent but more specialized care, while modern wool may need more regular attention but often with simpler methods.
Can Tweed Coats Be Modernized? Hybrid Options
The distinction between tweed and modern wool isn’t always clear-cut. Innovative designers and manufacturers have created compelling hybrid options that combine traditional tweed aesthetics with contemporary performance features.
Modern interpretations of tweed coats often feature:
* Lighter weight tweed fabrics (12-16 oz compared to traditional 18-22 oz)
* Slimmer cuts with less structure through the body
* Shortened lengths for greater mobility
* Simplified patterns that reference traditional tweed while appearing more contemporary
* Partial linings that reduce weight and improve breathability
Manufacturing innovations have addressed some traditional limitations:
* Softer finishing processes that reduce tweed’s characteristic roughness
* Tighter weaves that improve weather resistance without sacrificing breathability
* Blending small percentages of performance fibers for stretch and durability
* Pre-washing techniques that provide immediate softness without breaking-in period
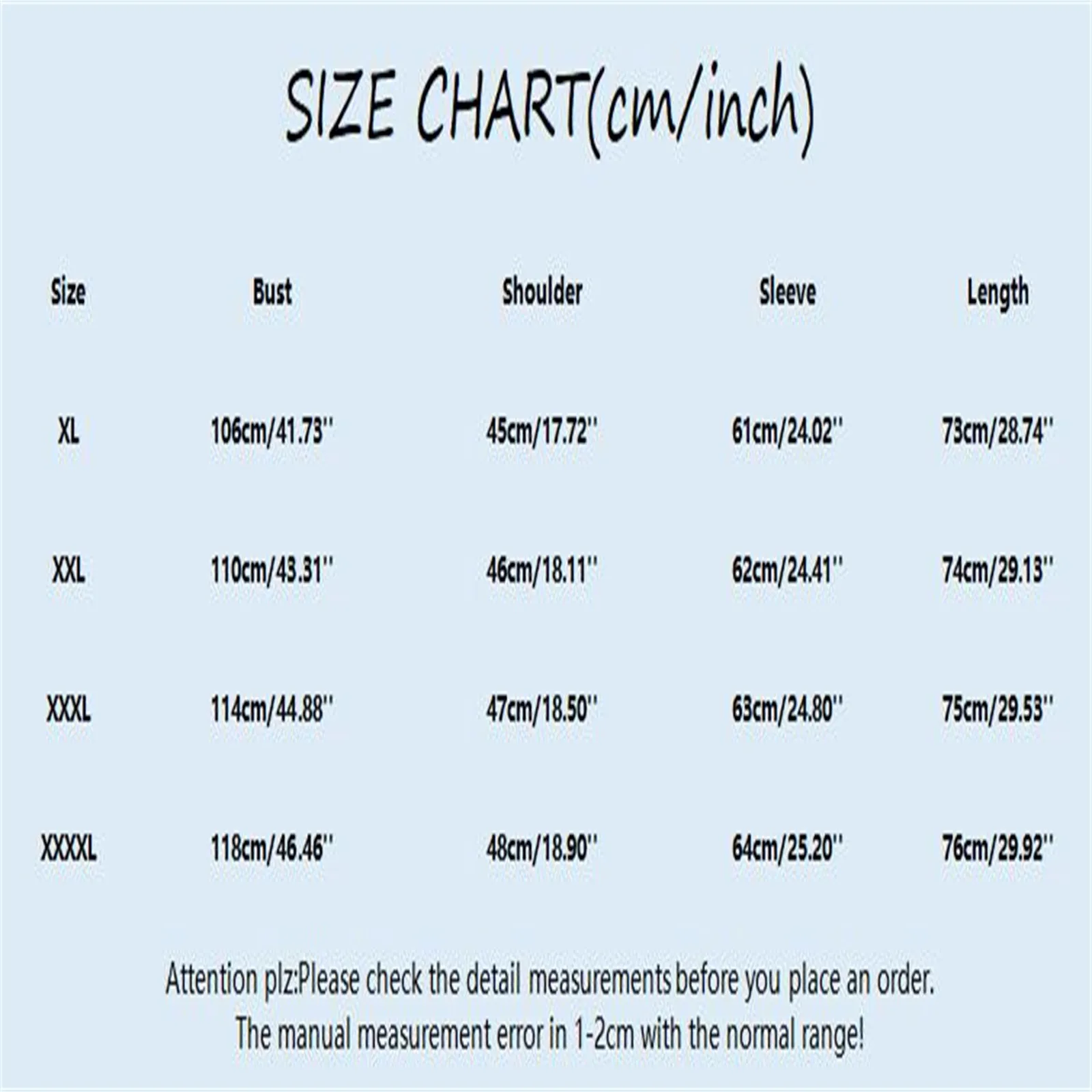
Designer approaches to modernizing tweed include:
* Unexpected color combinations that refresh traditional patterns
* Technical details like waterproof zippers or hidden media pockets
* Unconventional styling like asymmetric closures or stand collars
* Combining tweed panels with contrasting modern materials
Herringbone coats demonstrate this hybrid approach particularly well, featuring the distinctive pattern in lighter weight constructions and contemporary silhouettes. These adaptations preserve tweed’s character while addressing its traditional limitations, creating options that bridge the gap between heritage appeal and modern performance requirements.
Mens Double Breasted Pea Coat, Mens Wool Blend Coat, Mens Wool Pea Coat
Price range: $136.84 through $157.36 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageMens Cashmere Overcoat, Mens Hooded Winter Coat, Mens Wool Blend Coat
Price range: $128.72 through $139.68 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageMens Black Overcoat, Mens Black Wool Coat, Mens Wool Overcoat
$339.18 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageMens Grey Overcoat, Mens Wool Blend Coat, Mens Wool Overcoat
$201.28 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageMens Herringbone Coat, Mens Long Overcoat, Mens Wool Overcoat
Price range: $197.16 through $203.69 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageMens Long Overcoat, Mens Tweed Coat
Price range: $397.49 through $409.96 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
What Body Types and Heights Best Suit Each Coat Style?
Finding the most flattering coat involves considering how each style’s structure and visual characteristics interact with your physical proportions.
For Taller Men (6‘0”+)
* Traditional tweed overcoats: Full length styles balance tall frames
* Modern wool: Longer styles maintain proportion; avoid too-short coats that make limbs appear exaggerated
* Both styles work well, though tweed’s structure often complements height better
For Average Height (5‘8”-6‘0”)
* Traditional tweed: Mid-thigh to knee length most versatile
* Modern wool: Similar length recommendations, though slimmer cuts often more flattering
* Most versatile height range for either style
For Shorter Men (Under 5‘8”)
* Traditional tweed: Can appear overwhelming; choose shorter styles ending mid-thigh
* Modern wool: Advantage for shorter men due to less bulk and cleaner lines
* Vertical patterns like herringbone visually elongate the frame
For Athletic Builds
* Traditional tweed: Accommodates broader shoulders naturally; may require waist suppression
* Modern wool: Often requires tailoring to prevent boxy appearance on V-shaped torsos
* Both work well when properly fitted
For Slim Builds
* Traditional tweed: Adds desirable substance and visual weight
* Modern wool: Choose slightly structured versions to avoid appearing overwhelmed by the garment
* Layer underneath to create more substantial appearance
For Larger Builds
* Traditional tweed: Patterns can disguise weight; avoid bulky details
* Modern wool: Solid colors in structured styles create cleaner lines
* Single-breasted styles in either fabric generally more flattering than double-breasted
Understanding the perfect coat length for height significantly impacts how either material drapes and flatters your frame. The structure and weight of the fabric interact directly with body proportions – tweed’s substantial nature adds visual weight (beneficial for thin frames, potentially overwhelming for larger builds), while modern wool’s cleaner lines can streamline appearance (advantageous for larger frames, potentially insubstantial on very slim builds).
Are Modern Wool Coats Really Less Durable Than Tweed?
The common perception that tweed inherently outlasts modern wool deserves closer examination. While traditional tweed does possess remarkable longevity, several factors beyond fabric type determine a coat’s actual durability.
Construction Quality Trumps Material
Many modern wool coats fail prematurely not because of the wool itself but due to inferior construction. Key indicators of quality construction that affect longevity in any coat include:
* Fully canvassed or half-canvassed construction rather than fused
* Hand-sewn buttonholes that resist fraying
* Dense stitching (10+ stitches per inch)
* Reinforced stress points at pockets and vents
* Quality lining attached with sufficient allowance for movement
Hidden Durability Factors
Several less obvious elements significantly impact longevity:
* Button attachment method (cross-stitched buttons last longer)
* Presence of chain stitching at collar (prevents stretching)
* Properly secured lining that doesn’t place stress on outer fabric
* Adequate seam allowance permitting future alterations
Common Failure Points
For both coat types, typical wear appears first in predictable locations:
* Elbow wear (tweed often includes leather patches to address this)
* Collar creasing and shine from oils
* Pocket edge fraying from repeated use
* Button thread deterioration
* Lining wear at center back and armholes
High-quality modern wool coats with proper construction can indeed match tweed’s longevity. However, the average tweed coat is more likely to feature superior construction details as manufacturers expect and design for multi-decade use. The perception gap exists because many mass-market modern wool coats prioritize contemporary styling and price point over construction techniques that ensure longevity.
Can Tweed Coats Be Made Completely Weatherproof?
While traditional tweed provides impressive natural weather resistance, achieving complete weatherproofing requires understanding its inherent limitations and available enhancement options.
Traditional tweed offers moderate weather protection through:
* Natural lanolin content in wool fibers that repels light moisture
* Tight weave that blocks wind effectively
* Density that slows water penetration during brief exposure
Modern treatments can enhance tweed’s performance:
* Silicone-based water repellent sprays that increase surface tension
* Fluoropolymer treatments that create a protective barrier
* Wax-based treatments inspired by traditional methods
* Laminated waterproof membranes bonded to the tweed’s interior (in high-performance versions)
However, these enhancements come with tradeoffs:
* Most treatments require regular reapplication after cleaning
* Some treatments darken or change the fabric’s appearance slightly
* Membrane additions reduce breathability and alter the fabric’s natural drape
* Heavily treated tweed loses some of its characteristic texture and movement
Effective layering strategies enhance weather protection while maintaining authenticity:
* Waterproof shell layer over tweed for severe conditions
* Technical mid-layers beneath for additional insulation
* Waxed cotton or waterproof linings in key areas
When choosing between short versus long coats, consider that longer tweed styles provide better protection against driving rain but take longer to dry when wet. While tweed can be made significantly more weather-resistant, expecting complete weatherproofing equivalent to technical outerwear would require compromises that fundamentally alter what makes tweed special. For extreme conditions, layering approaches generally provide better results than attempting to transform tweed into something it fundamentally isn’t.
Which Coat Type Offers Better Value in Changing Fashion Trends?
Fashion resilience directly impacts long-term satisfaction and investment value when choosing between tweed and modern wool coats.
Tweed’s Trend Resilience
Tweed has demonstrated remarkable staying power through multiple fashion cycles:
* Established as a menswear staple for over 150 years
* Periodic resurgences as both heritage and ironic fashion statements
* Consistent presence in luxury and traditional menswear
* Connection to enduring British country aesthetic
While tweed never completely disappears from fashion, its prominence does fluctuate. Current trend indicators suggest continued strong presence in menswear through seasonal reinterpretations that reference its heritage while incorporating contemporary elements.
Modern Wool Coat Trend Patterns
Contemporary wool coats show more variability in fashion relevance:
* Clean, minimalist designs have shown remarkable staying power since the 1990s
* Technical wool blends gain/lose prominence with broader athleisure trends
* Silhouette changes (slim vs. oversized) cycle more noticeably than with tweed
* Color trends affect modern wool more significantly than patterned tweed
Adapting to Evolving Trends
Both coat types can be updated through:
* Contemporary styling with current accessories
* Modern layering techniques
* Strategic alterations to update length or silhouette
* Combining with unexpected complementary pieces
Tweed generally offers greater immunity to trend obsolescence through its distinctive character and established heritage associations. Modern wool coats in classic colors and cuts also demonstrate good trend resilience, while highly fashion-forward versions may date more quickly. The most trend-resistant choice in either category is a well-constructed coat in a classic silhouette with minimal fashion-specific details.
Making Your Decision: Questions to Consider
Choosing between tweed and modern wool requires honest assessment of your specific needs, preferences, and lifestyle:
Primary Environment Assessment
* Do you spend most time in urban settings or rural/outdoor environments?
* What’s the typical formality level of your daily activities?
* How much time do you spend outdoors versus in climate-controlled spaces?
Climate Considerations
* What temperature range do you typically experience during coat-wearing months?
* Is precipitation primarily rain, snow, or mixed?
* Do you face significant wind exposure?
* How quickly do conditions change throughout the day?
Style Preferences
* Do you prefer distinctive traditional patterns or clean minimalist aesthetics?
* Is your overall style more heritage-inspired or contemporary?
* Do you value distinctive character or versatile integration with varied outfits?
* How important is making a unique style statement versus blending in?
Maintenance Reality Check
* How willing are you to follow specialized care instructions?
* Do you have convenient access to quality dry cleaning services?
* Are you diligent about seasonal storage practices?
* Do you have adequate storage space for proper coat maintenance?
Budget Framework
* Are you willing to invest more upfront for potential longer lifespan?
* Is immediate versatility or long-term durability more financially important to you?
* Does your climate justify significant investment in a single high-quality coat?
The ideal decision balances these factors rather than focusing exclusively on any single consideration. Many discerning coat buyers ultimately invest in both styles over time: a quality tweed coat for specific occasions and seasonal wear, complemented by a versatile modern wool coat for everyday practicality.
Ethical and Sustainability Considerations
Environmental and ethical factors increasingly influence purchasing decisions for quality garments like wool coats.
Wool Sourcing and Animal Welfare
Both coat types use wool as their primary material, but sourcing standards vary:
* Responsible wool producers adhere to mulesing-free practices and humane shearing
* Certified wool programs like ZQ Merino and RWS (Responsible Wool Standard) ensure ethical treatment
* Heritage tweed producers often maintain direct relationships with specific farms and flocks
* Modern wool production may involve more complex supply chains with varying transparency
Production Environmental Impact
Manufacturing processes differ in environmental footprint:
* Traditional tweed production typically uses fewer chemical treatments but more water
* Modern wool processing may involve additional chemicals for performance enhancements
* Local production (common with heritage tweed) reduces transportation emissions
* Energy efficiency varies widely between modern factories and traditional workshops
Longevity as Sustainability
Perhaps the most significant sustainability factor is useful lifespan:
* A coat worn for 20+ years has dramatically lower environmental impact than multiple replacements
* Quality construction that permits repairs extends useful life substantially
* Classic styling that resists trend obsolescence prevents premature disposal
* End-of-life recyclability depends on material purity (pure wool is more readily recyclable)
Certifications Worth Considering
When evaluating ethical and sustainable production:
* RWS (Responsible Wool Standard) for animal welfare
* GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) for environmental processing
* Bluesign® for chemical management and worker safety
* Local craft certifications that preserve traditional skills and communities
The most sustainable coat is ultimately one that receives regular wear over many years. While manufacturing methods matter, choosing a coat you’ll wear frequently and maintain properly often represents the most environmentally responsible decision, regardless of whether it’s tweed or modern wool.







